https://www.blaney.com/articles/coronavirus-can-ontario-employees-refuse-to-work
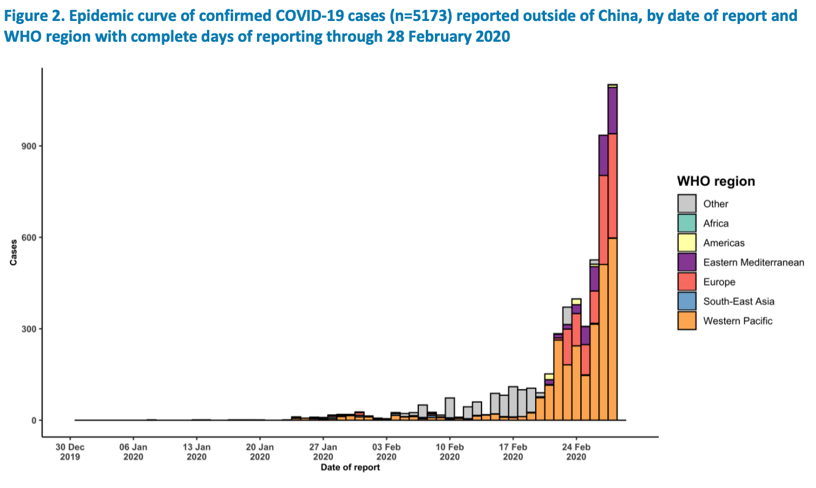
The World Health Organization (WHO) declared the Corona Virus outbreak a “Public Health Emergency of International Concern” on January 30th, 2020 (WHO, 2020). With the recent outbreak of the Coronavirus, Ontario employees are questioning if they are allowed to refuse to work. The article, titled “Canada: Coronavirus: Can Ontario Employees Refuse to Work?” investigates this question. With only one confirmed case in Ontario and nine under investigation (number subject to change), McClelland states that “the Coronavirus raises legitimate concern for both employees and employers in Ontario” (2020). The article enquires section 43 of the Occupational Health and Safety Act by the Government of Ontario, states that anyone who has reason to believe their work would endanger themselves, is entitled to refuse work (2018). However, McClelland believes that this refers to physical work hazard, not biological hazards. The following figure represents the growth of the virus since December 30th, 2019, until February 28th, 2020, provided by the World Health Organization (2020). The rapid exponential growth can be seen varying across many regions.
If an employee has reasonable grounds to refuse work, they must report to a supervisor who must then investigate with the worker and/or a health and safety representative. If the reasonable grounds are proven to be true, inspectors from the Ministry of Labour must be informed. McClelland continues to say that based on the current Coronavirus status in the province of Ontario, employers are likely to argue that their workplace is “no more susceptible than the general population and reasonable precautions are in place” and that “the employee’s mere anxiety” is not reasonable justification to refuse to work (2020).
With the frightening exponential spread of the virus, at what point can employees refuse work? The Occupational Health and Safety Act allows the employer to adhere to precautions that attend to the employees concerns. In this case, precautions can include stricter hygiene rules, provided face masks and provided gloves. McClelland evidently states that it is important to recognize this is a “temporary measure based on the threat” of the virus. While workers who are taking precautionary measures are put at ease, the question of healthcare workers arises. He states that “merely because a role is inherently dangerous does not eliminate or relax an employer’s obligations”. Therefore, if one is working in healthcare or an occupation that puts them at higher risk of being exposed to the virus, employers must ensure they are taking every precautionary measure in this especially hazardous environment.
If the case count continues to rise, especially in North America, it will be interesting to see how services such as coffee shops, fast food chains, and other locations such as schools will operate. With the risk for students travelling to various locations across the world, and the concentration of students with weakened immune systems due to being overworked, exhausted, and in dense populations, these health and safety measures are sure to come into question, we just are not sure of when.
References:
McClelland, C. (2020, February 25). Coronavirus: Can Ontario Employees Refuse to Work? Retrieved February 29, 2020, from https://www.blaney.com/articles/coronavirus-can-ontario-employees-refuse-to-work
Government of Ontario. (2018, November 19). Occupational Health and Safety Act. Retrieved February 29, 2020, from https://www.ontario.ca/laws/statute/90o01#BK81
World Health Organization. (2020, February 28). Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) – events as they happen. Retrieved February 29, 2020, from https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/events-as-they-happen